Posted in Networking on August 27, 2007|
Leave a Comment »
Types of Networking
One way to categorize the different types of computer network designs is by their scope or scale. For historical reasons, the networking industry refers to nearly every type of design as some kind of area network. Common examples of area network types are:
- LAN – Local Area Network
- WLAN – Wireless Local Area Network
- WAN – Wide Area Network
- MAN – Metropolitan Area Network
- SAN – Storage Area Network, System Area Network, Server Area Network, or sometimes Small Area Network
- CAN – Campus Area Network, Controller Area Network, or sometimes Cluster Area Network
- PAN – Personal Area Network
- DAN – Desk Area Network
LAN and WAN were the original categories of area networks, while the others have gradually emerged over many years of technology evolution.
For more details, click here.
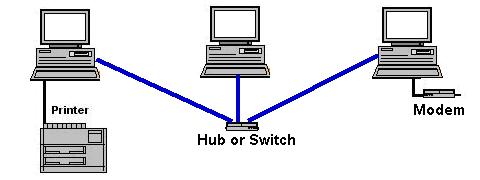
Computer Networking – How It Works?
Computer networking is a process of sharing data and shared resources between two or more connected computers. The shared resources can include printer, Fax modem, Hard disk, CD – DVD Rom, Database and the data files. A computer network can be divided into a small or local area network, a networking between computers in a building of a office (LAN), medium sized network (MAN), a network between two offices in a city and Wide network (WAN) a network between the computers, one is locally and the other can be thousands of miles away in any other country of the world.
(more…)
Read Full Post »